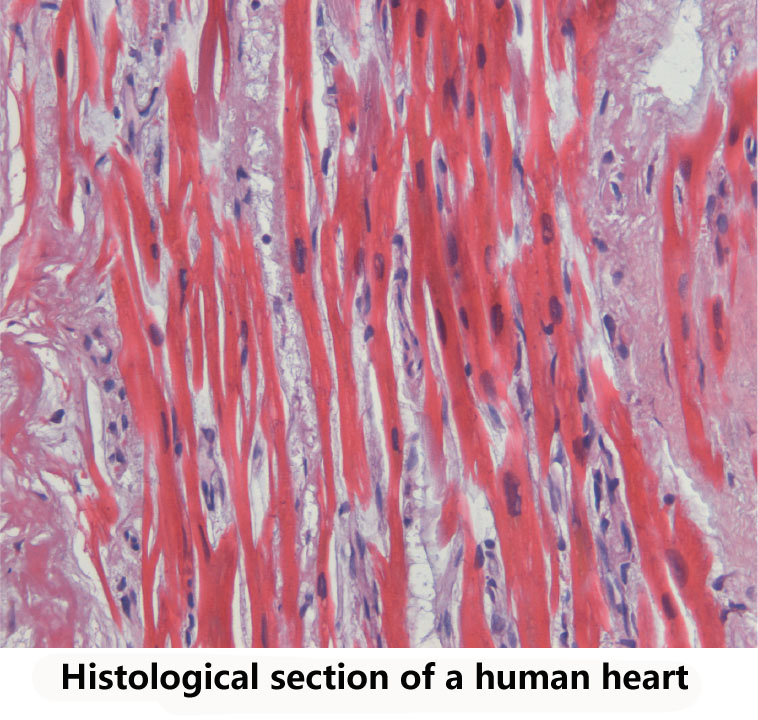
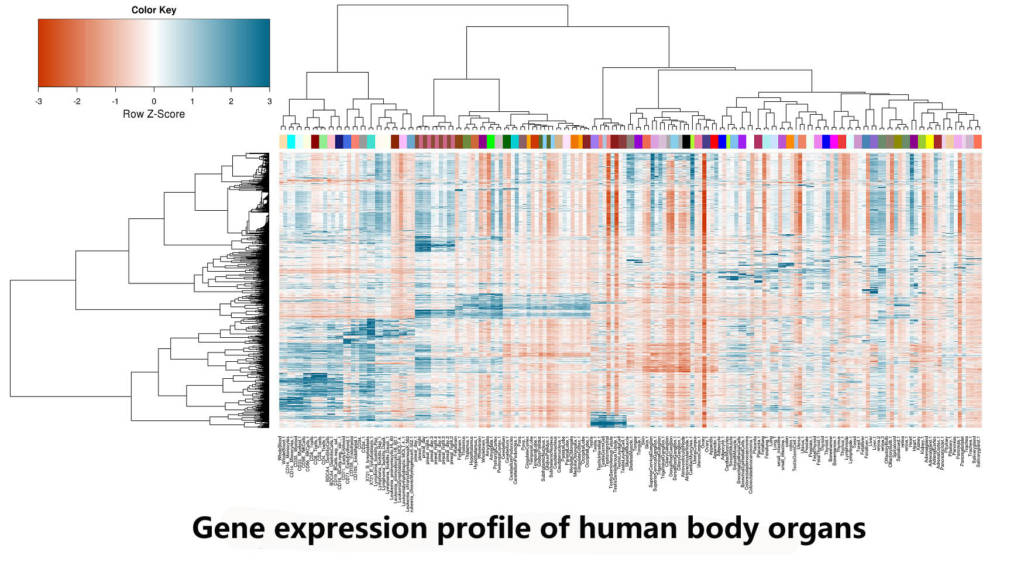
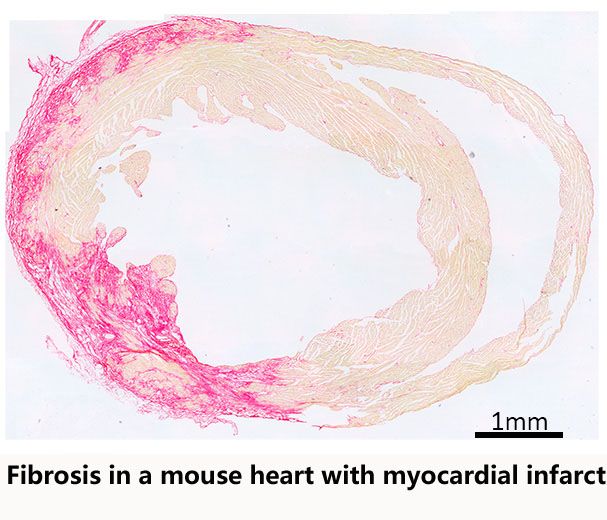
Heart failure epigenomics and molecular epigenetics
The human genome is organised into a tight nuclear space where genes and their functional elements interact to control gene expression. “Genome organisation” in space and time is also referred to as the epigenome. Strong emerging evidence suggest that the epigenome holds clues for important novel medical therapy. As part of fully annotating the epigenome of the heart, it is important to map all heart-relevant genes, their functional elements and to determine all relationships between them.
The mission in the Foo-lab, which moved from Cambridge UK and started in Singapore in 2013, is to understand “genome organisation” in heart cells. We are interested in how heart cells undergo “epigenomic remodelling” during the transition to heart disease: how this might lead to altered stress-gene responses, and how it contributes to heart failure disease progression. By exploring this area of research, we are particularly looking to discover novel mechanisms of disease that may offer new therapeutic options or new heart disease biomarkers. Our projects involve making use of the latest genomic technologies, human explanted tissue and animal disease models. We are always on a look-out to work with people who have the same interest in this area of research.


*stats from Singapore Heart Foundation.
Our lab has also been instrumental in putting together a clinical genomics programme starting with high-throughput genetic tests for patients with Inherited Cardiac Conditions (ICC). This has led to an ICC clinic which is run at the National University Heart Centre [link]. We are also working to apply Clinical Genomics as diagnostics in the Clinical Genetics Departments at NUHkids (with A/Prof Denise Goh) and KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital (with Drs Angeline Lai and Saumya Jamuar).
You can find us
Cardiac Epigenome
Key Research Programmes
Clinical Research
Note 1
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
NOTES
- As part of the SUREkids Rare Disease Programme.
- As part of the Inherited Cardiac Condition Clinic.
- Invented for ICC, exomes & genomes.
Discoveries


Viruses
Animals
Gene Engineering
Libraries sequenced